Slope stability
Undrained slope stability
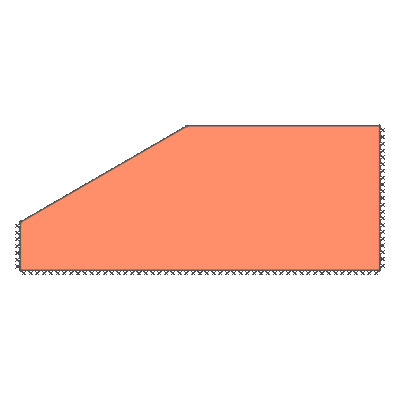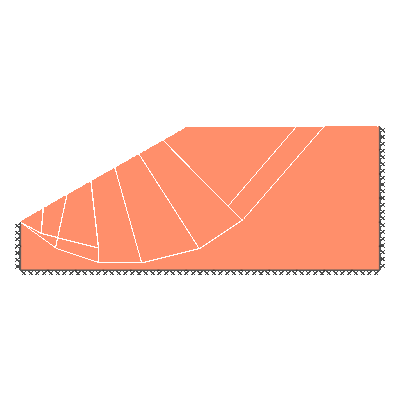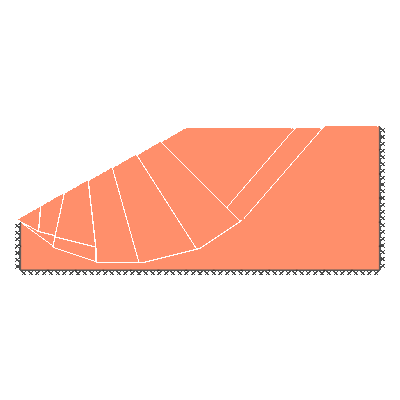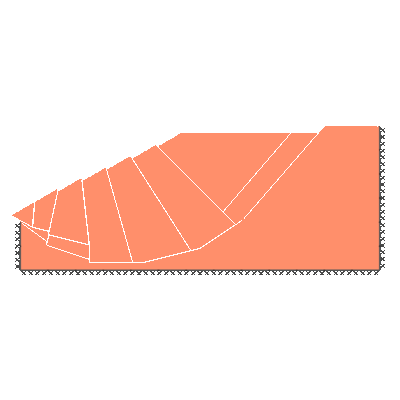
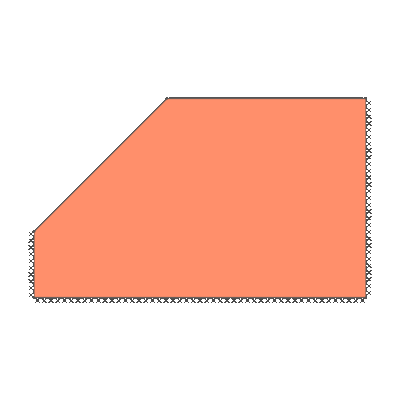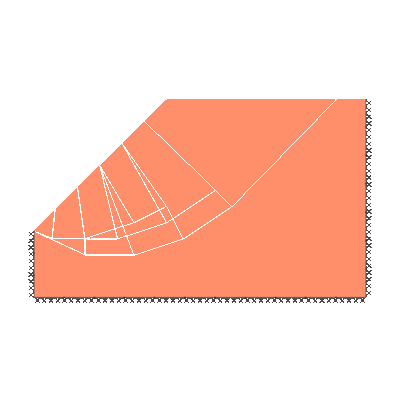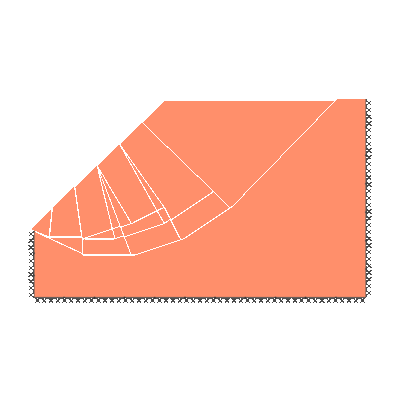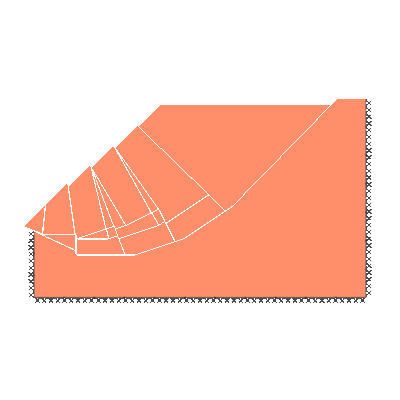
Undrained slope stability, 30 degree slope, failure through toe
| Benchmark | 6.51 |
| Result | 6.72 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 3.18% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 3.18% |
GENERAL DESCRIPTION: Slope stability problem, horizontal soil surface beyond crest, no soil beyond toe
ANALYSIS TYPE: Undrained, tension cutoff not modelled
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope height 1m; crest width = 1.5m; depth below toe 0.5m
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge
SOIL PROPERTIES: c_u = 1 kN/m2, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: 6.51
REFERENCE: Chen (2007). Limit Analysis and Soil Plasticity, J. Ross Publishing, Table 9.2.
Undrained slope stability, 45 degree slope, failure through toe
| Benchmark | 5.86 |
| Result | 6.08 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 3.54% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 3.54% |
GENERAL DESCRIPTION: Slope stability problem, horizontal soil surface beyond crest, no soil beyond toe
ANALYSIS TYPE: Undrained, tension cutoff not modelled
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope height 1m; crest width = 1.5m; depth below toe 0.5m
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge
SOIL PROPERTIES: c_u = 1 kN/m2, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: 5.86
REFERENCE: Chen (2007). Limit Analysis and Soil Plasticity, J. Ross Publishing, Table 9.2.
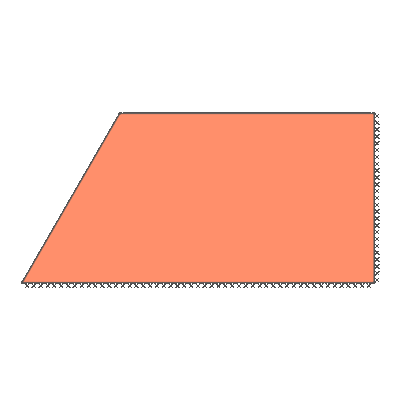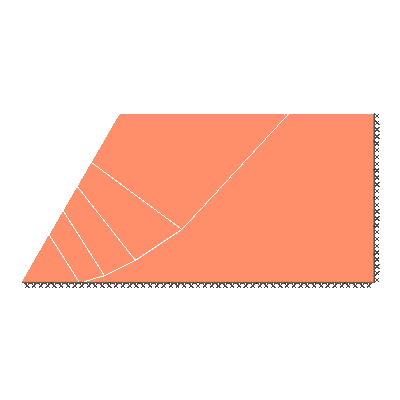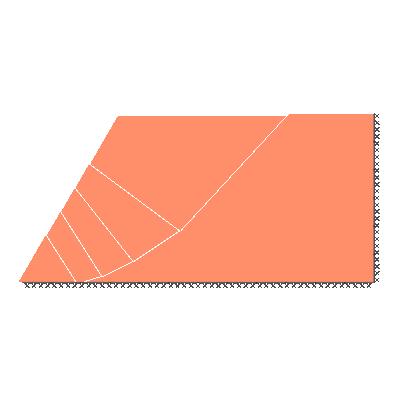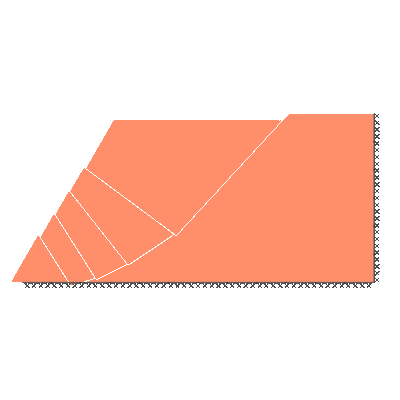
Undrained slope stability, 60 degree slope, rigid below level of toe
| Benchmark | 5.25 |
| Result | 5.35 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 1.96% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 1.96% |
GENERAL DESCRIPTION: Slope stability problem, horizontal soil surface beyond crest
ANALYSIS TYPE: Undrained, tension cutoff not modelled
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope height 1m; crest width = 1.5m; depth below toe 0m
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge
SOIL PROPERTIES: c_u = 1 kN/m2, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: 5.25
REFERENCE: Chen (2007). Limit Analysis and Soil Plasticity, J. Ross Publishing, Table 9.4.
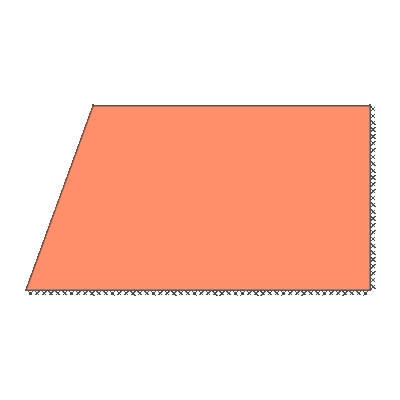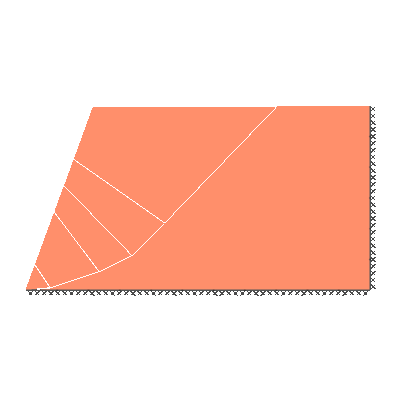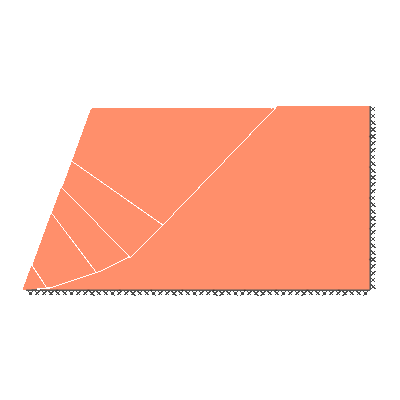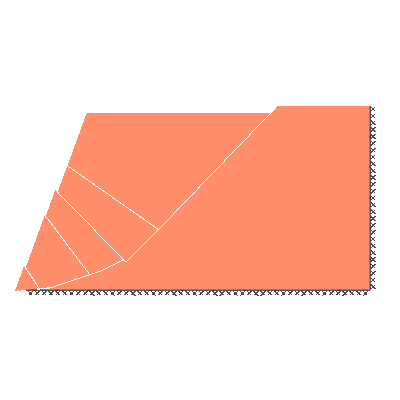
Undrained slope stability, 70 degree slope, rigid below level of toe
| Benchmark | 4.8 |
| Result | 4.85 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 1.1% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 1.1% |
GENERAL DESCRIPTION: Slope stability problem, horizontal soil surface beyond crest
ANALYSIS TYPE: Undrained, tension cutoff not modelled
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope height 1m; crest width = 1.5m; depth below toe 0m
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge
SOIL PROPERTIES: c_u = 1 kN/m2, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: 4.80
REFERENCE: Chen (2007). Limit Analysis and Soil Plasticity, J. Ross Publishing, Table 9.4.
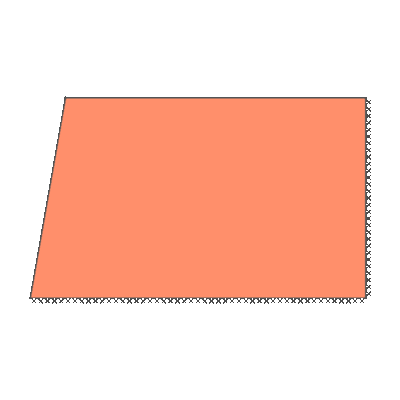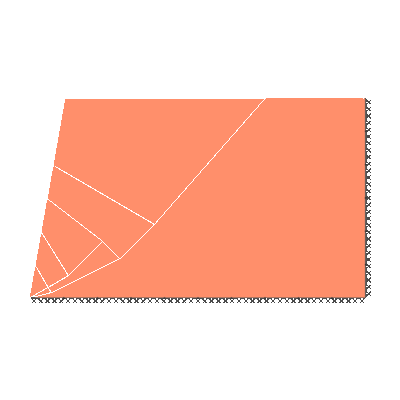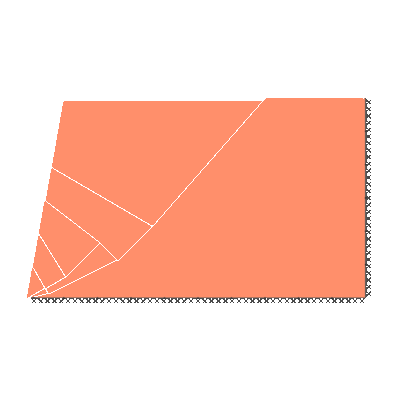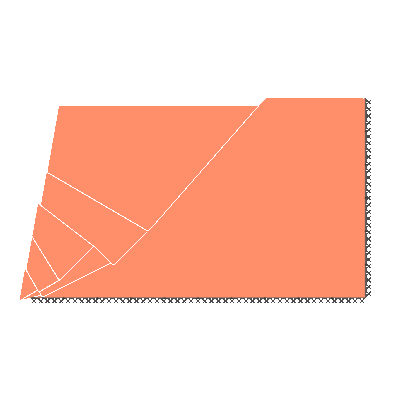
Undrained slope stability, 80 degree slope, rigid below level of toe
| Benchmark | 4.33 |
| Result | 4.34 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 0.33% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 0.33% |
GENERAL DESCRIPTION: Slope stability problem, horizontal soil surface beyond crest
ANALYSIS TYPE: Undrained, tension cutoff not modelled
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope height 1m; crest width = 1.5m; depth below toe 0m
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge
SOIL PROPERTIES: c_u = 1 kN/m2, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: 4.33
REFERENCE: Chen (2007). Limit Analysis and Soil Plasticity, J. Ross Publishing, Table 9.4.
Undrained slope stability, 90 degree slope, rigid below level of toe
| Benchmark | 3.79 |
| Result | 3.83 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 1.15% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 1.15% |
GENERAL DESCRIPTION: Slope stability problem, horizontal soil surface beyond crest
ANALYSIS TYPE: Undrained, tension cutoff not modelled
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope height 1m; crest width = 1.5m; depth below toe 0m
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge
SOIL PROPERTIES: c_u = 1 kN/m2, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: 3.83
REFERENCE: Chen (2007). Limit Analysis and Soil Plasticity, J. Ross Publishing, Table 9.4.
Drained slope stability (dry slopes)
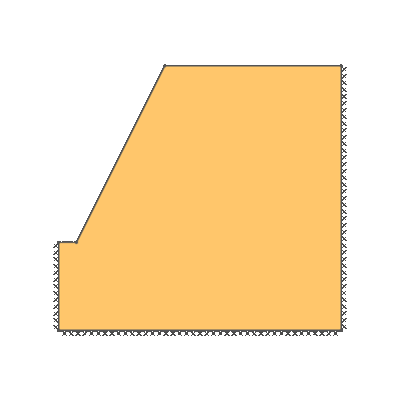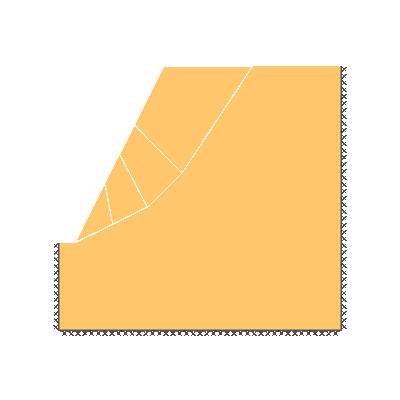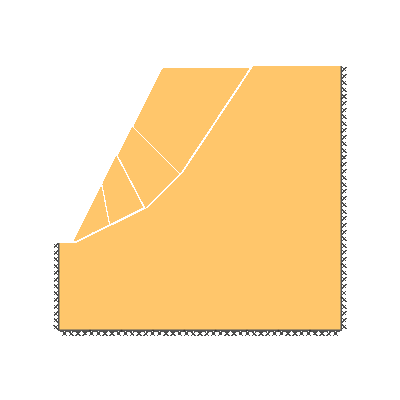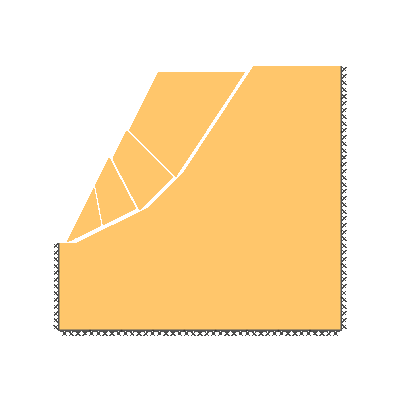
Drained 0.5:1.0 slope, phi'=20 degrees, c'/gamma H = 0.15
| Benchmark | 1 |
| Result | 1.06 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 5.84% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 4.1% |
ANALYSIS TYPE: Drained.
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope angle, cot beta = 0.5:1.0 (63.4 degrees), slope height, H = 1m, width beyond crest = 1m, total soil depth, D = 1.5m.
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight.
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge.
WATER REGIME: Zero pore water pressures
SOIL PROPERTIES: c'=0.15 kN/m2, phi' = 20 degrees, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3.
PARTIAL FACTOR SET: User.
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: Factor on soil strength 1.25 (D=1 solution most critical). Here this factor is applied via partial factor set 'User'.
NOTES: Factor on soil strength of 1.250 gives adequacy factor of 1.06, i.e. error on soil self weight of 6%. 'Benchmark' partial factor set with factor of 1.301 on c' and tan(phi') is required to give adequacy factor of 1.000. Corresponding error on input parameters = 4.1%.
REFERENCE: Whitlow, R. (1990) Basic soil mechanics (2nd edition), Longman.
COMMENT: Benchmark based on Bishops method (limit equilibrium).
Drained 0.5:1.0 slope, phi'=30 degrees, c'/gamma H = 0.15
| Benchmark | 1 |
| Result | 1.05 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 4.84% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 2.9% |
ANALYSIS TYPE: Drained.
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope angle, cot beta = 0.5:1.0 (63.4 degrees), slope height, H = 1m, width beyond crest = 1m, total soil depth, D = 1.5m.
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight.
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge.
WATER REGIME: Zero pore water pressures
SOIL PROPERTIES: c'=0.15 kN/m2, phi' = 30 degrees, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3.
PARTIAL FACTOR SET: User.
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: Factor on soil strength 1.5 (D=1 solution most critical). Here this factor is applied via partial factor set 'User'.
NOTES: Factor on soil strength of 1.50 gives adequacy factor of 1.05, i.e. error on soil self weight of 5%. 'Benchmark' partial factor set with factor of 1.544 on c' and tan(phi') is required to give adequacy factor of 1.000. Corresponding error on input parameters = 2.9%.
REFERENCE: Whitlow, R. (1990) Basic soil mechanics (2nd edition), Longman.
COMMENT: Benchmark based on Bishops method (limit equilibrium).
Drained 0.5:1.0 slope, phi'=40 degrees, c'/gamma H = 0.15
| Benchmark | 1 |
| Result | 1.02 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 1.99% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 1.1% |
ANALYSIS TYPE: Drained.
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope angle, cot beta = 0.5:1.0 (63.4 degrees), slope height, H = 1m, width beyond crest = 1m, total soil depth, D = 1.5m.
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight.
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge.
WATER REGIME: Zero pore water pressures
SOIL PROPERTIES: c'=0.15 kN/m2, phi' = 40 degrees, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3.
PARTIAL FACTOR SET: User.
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: Factor on soil strength 1.80 (D=1 solution most critical). Here this factor is applied via partial factor set 'User'.
NOTES: Factor on soil strength of 1.800 gives adequacy factor of 1.02, i.e. error on soil self weight of 2%. 'Benchmark' partial factor set with factor of 1.820 on c' and tan(phi') is required to give adequacy factor of 1.000. Corresponding error on input parameters = 1.1%.
REFERENCE: Whitlow, R. (1990) Basic soil mechanics (2nd edition), Longman.
COMMENT: Benchmark based on Bishops method (limit equilibrium).
Drained 1.0:1.0 slope, phi'=20 degrees, c'/gamma H = 0.15
| Benchmark | 1 |
| Result | 1.09 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 8.31% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 5.3% |
ANALYSIS TYPE: Drained.
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope angle, cot beta = 1.0:1.0 (45 degrees), slope height, H = 1m, width beyond crest = 1m, total soil depth, D = 1.5m.
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight.
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge.
WATER REGIME: Zero pore water pressures
SOIL PROPERTIES: c'=0.15 kN/m2, phi' = 20 degrees, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3.
PARTIAL FACTOR SET: User.
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: Factor on soil strength 1.58 (D=1 solution most critical). Here this factor is applied via partial factor set 'User'.
NOTES: Factor on soil strength of 1.580 gives adequacy factor of 1.09, i.e. error on soil self weight of 9%. 'Benchmark' partial factor set with factor of 1.660 on c' and tan(phi') is required to give adequacy factor of 1.000. Corresponding error on input parameters = 5.3%.
REFERENCE: Whitlow, R. (1990) Basic soil mechanics (2nd edition), Longman.
COMMENT: Benchmark based on Bishops method (limit equilibrium).
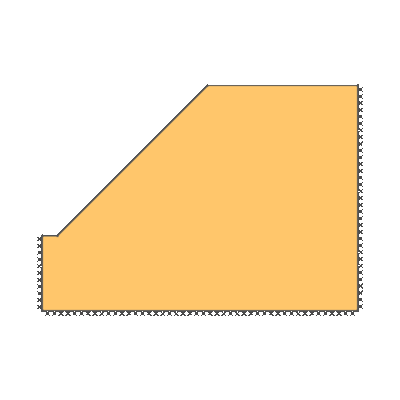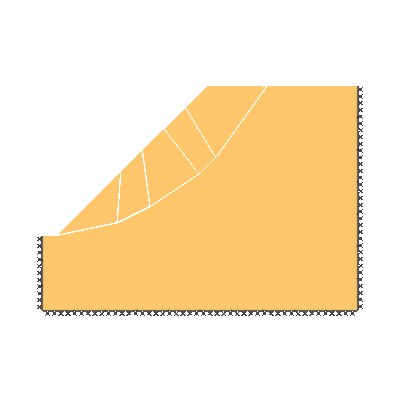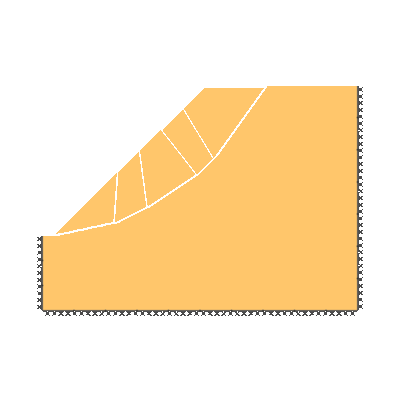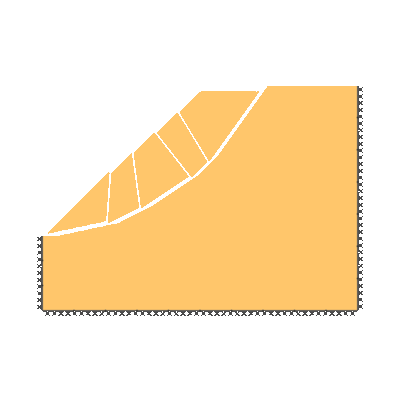
Drained 1.0:1.0 slope, phi'=30 degrees, c'/gamma H = 0.15
| Benchmark | 1 |
| Result | 1.11 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 9.77% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 5.8% |
ANALYSIS TYPE: Drained.
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope angle, cot beta = 1.0:1.0 (45 degrees), slope height, H = 1m, width beyond crest = 1m, total soil depth, D = 1.5m.
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight.
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge.
WATER REGIME: Zero pore water pressures
SOIL PROPERTIES: c'=0.15 kN/m2, phi' = 30 degrees, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3.
PARTIAL FACTOR SET: User.
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: Factor on soil strength 1.93 (D=1 solution most critical). Here this factor is applied via partial factor set 'User'.
NOTES: Factor on soil strength of 1.930 gives adequacy factor of 1.11, i.e. error on soil self weight of 11%. 'Benchmark' partial factor set with factor of 2.041 on c' and tan(phi') is required to give adequacy factor of 1.000. Corresponding error on input parameters = 5.8%.
REFERENCE: Whitlow, R. (1990) Basic soil mechanics (2nd edition), Longman.
COMMENT: Benchmark based on Bishops method (limit equilibrium).
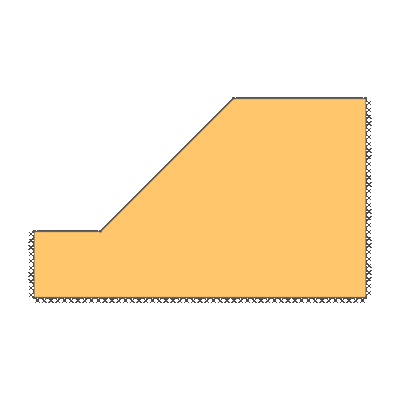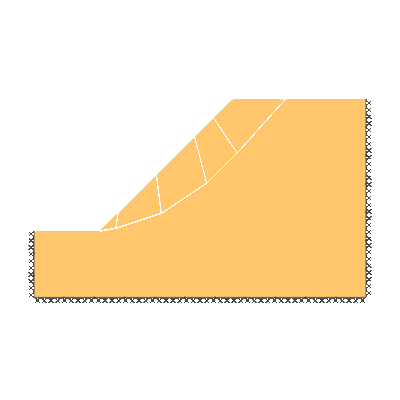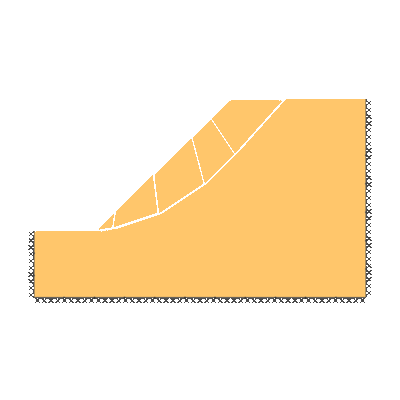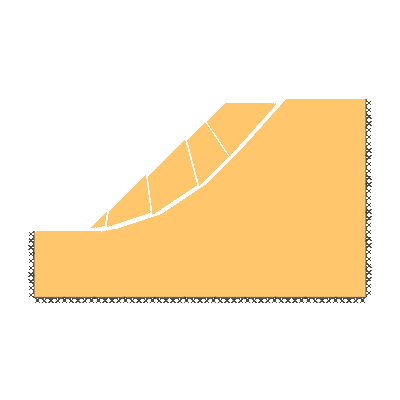
Drained 1.0:1.0 slope, phi'=40 degrees, c'/gamma H = 0.15
| Benchmark | 1 |
| Result | 1.1 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 9.38% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 4.9% |
ANALYSIS TYPE: Drained.
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope angle, cot beta = 1.0:1.0 (45 degrees), slope height, H = 1m, width beyond crest = 1m, total soil depth, D = 1.5m.
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight.
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge.
WATER REGIME: Zero pore water pressures
SOIL PROPERTIES: c'=0.15 kN/m2, phi' = 40 degrees, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3.
PARTIAL FACTOR SET: User.
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: Factor on soil strength 2.33 (D=1 solution most critical). Here this factor is applied via partial factor set 'User'.
NOTES: Factor on soil strength of 2.330 gives adequacy factor of 1.10, i.e. error on soil self weight of 10%. 'Benchmark' partial factor set with factor of 2.445 on c' and tan(phi') is required to give adequacy factor of 1.000. Corresponding error on input parameters = 4.9%.
REFERENCE: Whitlow, R. (1990) Basic soil mechanics (2nd edition), Longman.
COMMENT: Benchmark based on Bishops method (limit equilibrium).
Drained slope stability (with ru coefficient)
Drained 0.5:1.0 slope, phi'=20 degrees, c'/gamma H = 0.15, ru=0.25
| Benchmark | 1 |
| Result | 1.07 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 6.73% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 5.6% |
ANALYSIS TYPE: Drained.
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope angle, cot beta = 0.5:1.0 (63.4 degrees), slope height, H = 1m, width beyond crest = 1m, total soil depth, D = 1.5m.
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight.
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge.
WATER REGIME: ru = 0.25
SOIL PROPERTIES: c'=0.15 kN/m2, phi' = 20 degrees, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3.
PARTIAL FACTOR SET: User.
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: Factor on soil strength (1.25 - 0.25x0.81) = 1.0475 (D=1 solution most critical). Here this factor is applied via partial factor set 'User'.
NOTES: Factor on soil strength of 1.0475 gives adequacy factor of 1.07, i.e. error on soil self weight of 7%. 'Benchmark' partial factor set with factor of 1.106 on c' and tan(phi') is required to give adequacy factor of 1.000. Corresponding error on input parameters = 5.6%.
REFERENCE: Whitlow, R. (1990) Basic soil mechanics (2nd edition), Longman.
COMMENT: Benchmark based on Bishops method (limit equilibrium).
Drained 0.5:1.0 slope, phi'=30 degrees, c'/gamma H = 0.15, ru=0.25
| Benchmark | 1 |
| Result | 1.06 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 5.22% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 3.9% |
ANALYSIS TYPE: Drained.
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope angle, cot beta = 0.5:1.0 (63.4 degrees), slope height, H = 1m, width beyond crest = 1m, total soil depth, D = 1.5m.
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight.
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge.
WATER REGIME: ru = 0.25
SOIL PROPERTIES: c'=0.15 kN/m2, phi' = 30 degrees, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3.
PARTIAL FACTOR SET: User.
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: Factor on soil strength (1.5-0.25x1.25) = 1.1875 (D=1 solution most critical). Here this factor is applied via partial factor set 'User'.
NOTES: Factor on soil strength of 1.1875 gives adequacy factor of 1.06, i.e. error on soil self weight of 6%. 'Benchmark' partial factor set with factor of 1.234 on c' and tan(phi') is required to give adequacy factor of 1.000. Corresponding error on input parameters = 3.9%.
REFERENCE: Whitlow, R. (1990) Basic soil mechanics (2nd edition), Longman.
COMMENT: Benchmark based on Bishops method (limit equilibrium).
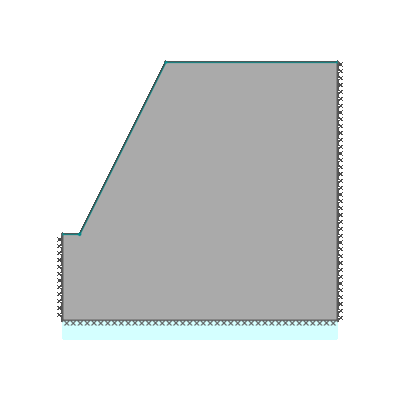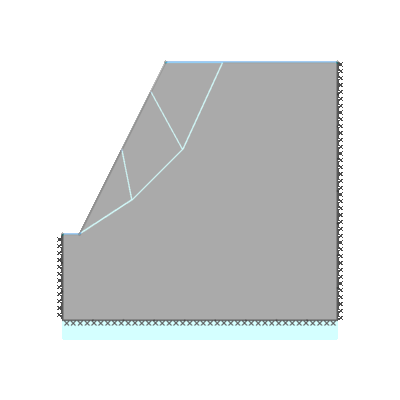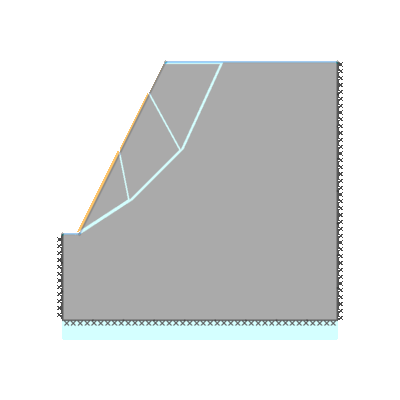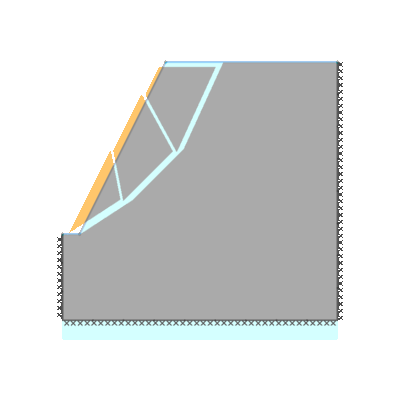
Drained 0.5:1.0 slope, phi'=40 degrees, c'/gamma H = 0.15, ru=0.25
| Benchmark | 1 |
| Result | 1.04 |
| Discrepancy on Collapse Load | 3.46% |
| Discrepancy on Input Parameters | 2.6% |
ANALYSIS TYPE: Drained.
KEY DIMENSIONS: Slope angle, cot beta = 0.5:1.0 (63.4 degrees), slope height, H = 1m, width beyond crest = 1m, total soil depth, D = 1.5m.
ADEQUACY FACTOR LOADING: Applied to soil self weight.
BOUNDARY CONDITIONS: No surcharge.
WATER REGIME: ru = 0.25
SOIL PROPERTIES: c'=0.15 kN/m2, phi' = 40 degrees, soil unit weight = 1 kN/m3.
PARTIAL FACTOR SET: User.
BENCHMARK SOLUTION: Factor on soil strength (1.80-0.25x1.82) = 1.345 (D=1 solution most critical). Here this factor is applied via partial factor set 'User'.
NOTES: Factor on soil strength of 1.345 gives adequacy factor of 1.04, i.e. error on soil self weight of 4%. 'Benchmark' partial factor set with factor of 1.380 on c' and tan(phi') is required to give adequacy factor of 1.000. Corresponding error on input parameters = 2.6%.
REFERENCE: Whitlow, R. (1990) Basic soil mechanics (2nd edition), Longman.
COMMENT: Benchmark based on Bishops method (limit equilibrium).